If you want to improve your skin texture, tone, and clarity, consider adding an acid to your skincare routine. But not all acids are created equal, and choosing the wrong one can lead to irritation, dryness, or even more skin problems. This article will compare and contrast two popular alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) types: Mandelic Acid or Glycolic Acid.
We will explain what they are, how they work, and what benefits they offer for different skin types and concerns. We will also help you decide which one is right for you and how to use it safely and effectively.
What is Mandelic Acid?
Mandelic acid is a type of alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) that comes from bitter almonds. It is a gentle exfoliant that helps to remove dead skin cells and improve skin texture. Mandelic acid also has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties that can help with acne and redness. Mandelic acid is suitable for sensitive and darker skin tones, unlike some other AHAs, as it does not cause irritation or hyperpigmentation.
Benefits of Mandelic Acid
- Exfoliation: Mandelic acid helps to dissolve the bonds between skin cells and reveals a smoother and brighter complexion. It can also reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles by stimulating collagen production.
- Anti-aging: Mandelic acid can help to fade dark spots and even out skin tone by inhibiting melanin production. It can also protect the skin from free radical damage and environmental stressors.
- Acne-fighting: Mandelic acid can help to clear clogged pores and prevent breakouts by reducing sebum production and killing acne-causing bacteria. It can also soothe inflammation and heal acne scars.
Who Can Use Mandelic Acid?
- Sensitive: Mandelic acid is less irritating than other AHAs because it has a larger molecular size and penetrates the skin more slowly and evenly. It also has anti-inflammatory effects that can calm sensitive skin.
- Acne-prone: Mandelic acid is effective against acne because it has antibacterial and sebum-regulating properties. It can also help to prevent post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation that often occurs after acne lesions heal.
- Darker: Mandelic acid is safe for darker skin tones because it does not cause melanotoxicity or increase the risk of hyperpigmentation. It can also help to lighten existing discoloration and improve skin radiance.
What is Glycolic Acid?
Glycolic acid is alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) that can help improve your skin’s appearance and texture. It dissolves the bonds between dead skin cells, making them easier to remove and revealing smoother, brighter, and younger-looking skin underneath.
- Exfoliation: Glycolic acid helps remove the outer layer of dead skin cells, which can clog pores and cause dullness. This can also improve the absorption of other skincare products and prevent acne breakouts.
- Brightening: Glycolic acid can reduce the appearance of dark spots, hyperpigmentation, and uneven skin tone by stimulating cell turnover and increasing collagen production.
- Anti-aging: Glycolic acid can smooth out fine lines and wrinkles by boosting collagen and elastin synthesis, essential for keeping the skin firm and elastic.
Glycolic acid is suitable for most skin types but especially for oily or sun-damaged skin. Oily skin can benefit from glycolic acid’s ability to unclog pores and regulate sebum production. Sun-damaged skin can benefit from glycolic acid’s ability to fade sun spots and improve skin texture.
However, glycolic acid is not recommended for sensitive or dry skin, as it can cause irritation, redness, and dryness. It is also essential to use sunscreen when using glycolic acid products, as they can make the skin more sensitive to sun exposure and increase the risk of sunburn.
Suppose you are interested in trying glycolic acid products. Start with a low concentration (5% or less) and gradually increase it as your skin adapts. You should also use glycolic acid products sparingly (once or twice a week) and follow them with a moisturizer to hydrate your skin.
Glycolic acid is a powerful ingredient that can transform your skin in many ways. By following these tips, you can enjoy the benefits of glycolic acid without compromising your skin’s health and safety.
Mandelic Acid or Glycolic Acid: Key Differences
Suppose you want to improve your skin texture, brightness, and appearance. In that case, you might be interested in using products that contain alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs). AHAs are chemical exfoliants that help remove dead skin cells and reveal smoother, fresher skin underneath. But not all AHAs are the same.
This section will compare and contrast two popular AHAs: Mandelic acid and Glycolic acid. We will look at their molecular structure, pH level, penetration depth, and potential side effects.
Molecular Structure
Mandelic acid and glycolic acid have different molecular structures that affect how they work on the skin. Mandelic acid is derived from bitter almonds and has a large molecular size of 152 Daltons. This means it penetrates the skin more slowly and gently than other AHAs. Glycolic acid is derived from sugar cane and has a small molecular size of 76 Daltons. This means it penetrates the skin more quickly and deeply than other AHAs.
pH Level
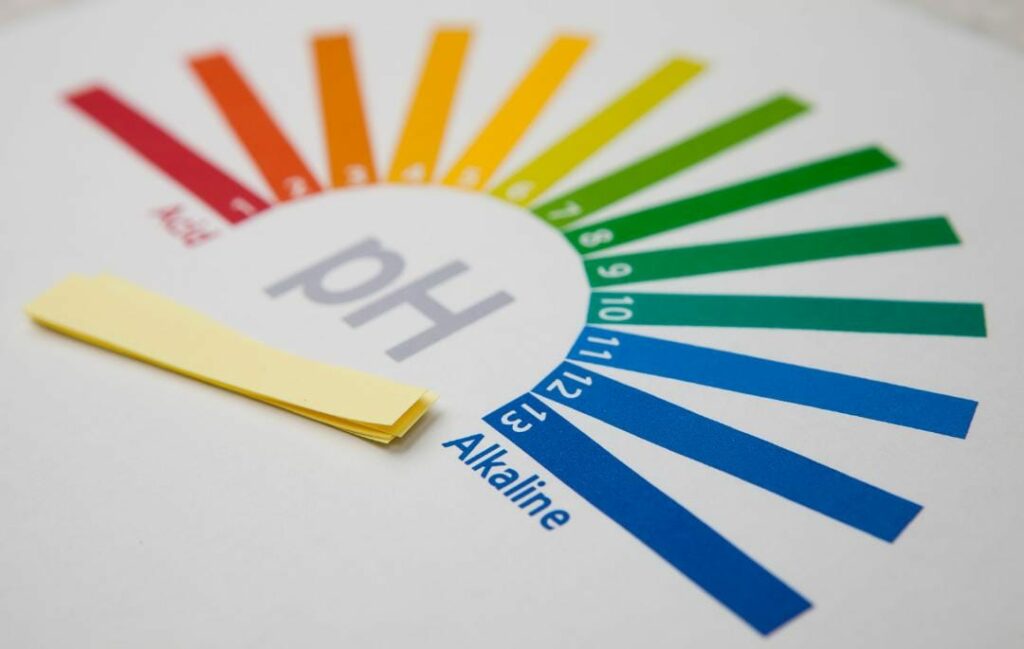
The pH level of an AHA product determines how acidic it is and how effective it is at exfoliating the skin. The lower the pH, the more cutting and potent the product. Mandelic acid and glycolic acid have different pH levels that affect their performance.
Mandelic acid has a pH of around 3.4, which is relatively high for an AHA. This means it is less irritating and more suitable for sensitive skin. Glycolic acid has a pH of around 2.0, which is relatively low for an AHA. This means it is more aggressive and more effective at resurfacing the skin.
Penetration Depth
The penetration depth of an AHA product determines how deep it can reach into the skin layers and how much it can affect the skin cells. The deeper the penetration, the more dramatic the results. Mandelic acid and glycolic acid have different penetration depths that affect their outcomes. Mandelic acid mainly works on the outermost layer of the skin, called the epidermis.
It helps with mild to moderate acne, hyperpigmentation, fine lines, and wrinkles. Glycolic acid can reach the epidermis and the middle layer of the skin, called the dermis. It helps with severe acne, sun damage, scarring, collagen production, and skin elasticity.
Potential Side Effects
Like any AHA product, mandelic acid and glycolic acid can cause some side effects on the skin, such as irritation, dryness, redness, peeling, or sensitivity to sunlight. However, these side effects vary depending on the type of AHA used.
Mandelic acid is generally considered gentler and safer than glycolic acid, especially for sensitive skin.
It causes less inflammation and has antibacterial properties that can prevent infections. Glycolic acid is generally considered harsher and riskier than Mandelic acid, especially for dark or reactive skin. It causes more irritation and can trigger hyperpigmentation or allergic reactions.
Mandelic and glycolic acids are effective AHAs that can improve your skin condition differently. However, they also have other characteristics that make them more or less suitable for different skin types and concerns. Before choosing an AHA product, consult your dermatologist or do a patch test to see how your skin reacts.
If you want to improve your skin texture, tone, and brightness, try using acid in your skincare routine. Acids are chemical exfoliants that help remove dead skin cells, unclog pores, and fade dark spots. But not all acids are the same, and choosing the wrong one can cause irritation, dryness, or even damage to your skin. In this section, we will guide you in choosing between two prevalent acids: Mandelic acid and Glycolic acid.
We will also discuss incorporating the preferred acid into your skincare routine, including frequency and concentration levels.
Mandelic Acid vs Glycolic Acid
Mandelic acid and glycolic acid are alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), which means they dissolve the bonds between the dead skin cells on the surface of your skin. However, they have different molecular sizes and strengths. Mandelic acid has a larger molecule than glycolic acid, penetrating the skin more slowly and gently. This makes it suitable for sensitive skin types or those new to acids. Mandelic acid also has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties, which can help with acne and rosacea.
Glycolic acid has a smaller molecule than mandelic acid, penetrating the skin more quickly and deeply. This makes it more effective for treating signs of aging, such as wrinkles, fine lines, and sun damage. Glycolic acid also stimulates collagen production, improving skin elasticity and firmness. However, glycolic acid can also irritate and dry some skin types, primarily if used too often or at high concentrations.
How to Choose the Right Acid for Your Skin
The best way to choose a suitable acid for your skin is to consider your skin type, concerns, and sensitivity level. Here are some general guidelines:
- Start with mandelic acid if you have dry, sensitive, or acne-prone skin. It is less likely to cause irritation or inflammation and can help soothe and hydrate your skin.
- Try glycolic acid if you have oily, mature, or dull skin. It is more powerful and can help reduce oiliness, smooth wrinkles, and brighten your complexion.
- If you have a combination or normal skin, you can use either mandelic or glycolic acid, depending on your preference and goals. You can also alternate between them or use them together in different routine steps.
How to Incorporate the Chosen Acid into Your Skincare Routine
Once you have chosen the suitable acid for your skin, you must know how to use it safely and effectively in your skincare routine. Here are some tips:
- Start with a low concentration and frequency. For example, you can use a 5% mandelic or glycolic acid toner once or twice a week at night. Gradually increase engagement and frequency as your skin tolerates it. Do not use more than 10% mandelic or glycolic acid at home unless directed by a dermatologist.
- Always patch test before using a new product. Apply a small amount of the product on an inconspicuous area of your skin and wait 24 hours to see any reaction. If you experience redness, itching, burning, or peeling, stop using the product immediately and consult a doctor.
- Always use sunscreen during the day when using acids. Acids can make your skin more sensitive to the sun and increase the risk of sunburns and hyperpigmentation. Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 every morning and reapply every two hours or as needed.
- Always moisturize after using acids. Acids can dry out your skin and compromise its moisture barrier. To prevent dehydration and irritation, apply a hydrating moisturizer after using an acid product. Look for ingredients like hyaluronic acid, ceramides, or squalane that can replenish and protect your skin.
- Always listen to your skin and adjust accordingly. If you notice any signs of over-exfoliation, such as tightness, flakiness, sensitivity, or breakouts, reduce the frequency or concentration of your acid product or take a break until your skin recovers.
Acids can be a great addition to your skincare routine if you choose the right one for your skin type and concerns. Mandelic acid is gentler and more suitable for sensitive or acne-prone skin. In contrast, glycolic acid is more robust and convenient for oily or aging skin.
Takeaway
both Mandelic Acid and Glycolic Acid are excellent options for achieving smooth, radiant skin. Mandelic Acid is a milder exfoliant that’s perfect for those with sensitive or acne-prone skin, as it’s less likely to cause irritation. On the other hand, Glycolic Acid is a more potent exfoliant that can effectively treat signs of aging, hyperpigmentation, and acne, but may be too harsh for those with sensitive skin.
Mandelic acid and glycolic acid are great ingredients that help you achieve smoother, brighter, and younger-looking skin. You can enjoy the benefits without the drawbacks by choosing the suitable acid for your skin. Happy exfoliating!